

Figure 2.5 Various relations between two vectors \overset has a magnitude of 6. A zero vector or a null vector is defined as a vector in space that has a magnitude equal to 0 and an undefined direction.

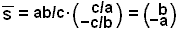
Calculate the dot-product between the vectors a × b and c to get the. Zero Vector or null vector is a vector which has zero magnitude and an arbitrary direction. Subtracting a number with a positive number gives the same result as adding a negative number of exactly the same number. Given the equation y C y 2 3 x 4 find a curve orthogonal to the given curve. These operators can also represent physical properties of a system that can be experimentally. Absolute values of two vectors are equal but when the direction is opposite they are called opposite vectors. Vectors are geometric representations of magnitude and direction which are often represented by straight arrows, starting at one point on a coordinate axis and ending at a different point. Operators in quantum mechanics are mathematical entities used to represent physical processes that result in the change of the state vector of the system, such as the evolution of these states with time. Does the odometer in an automobile indicate a scalar or a vector quantity? When adding many vectors in one dimension, it is convenient to use the concept of a unit vector.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
